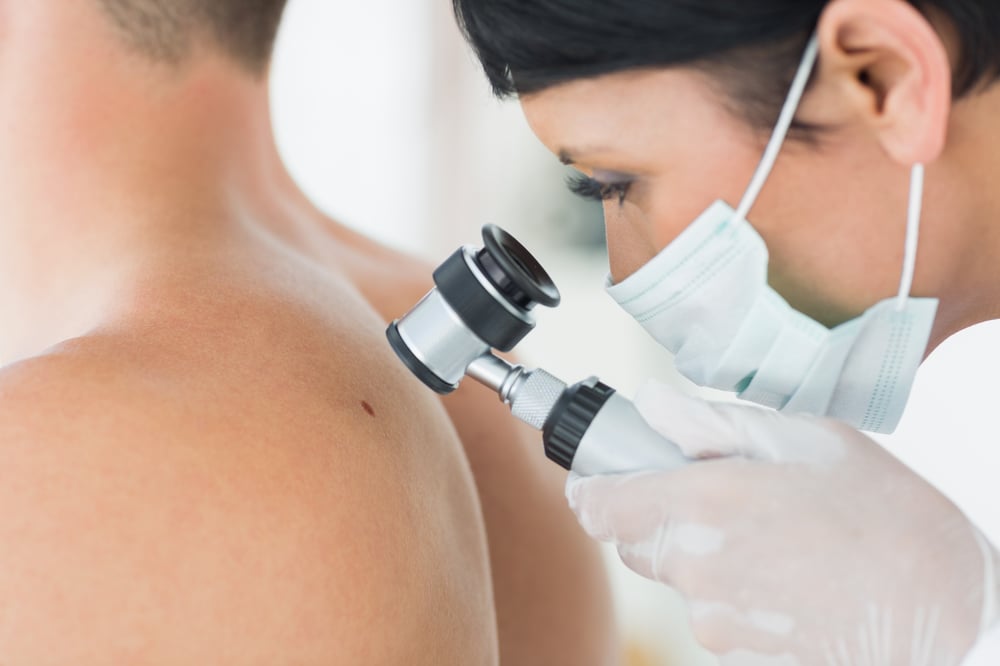
Melanoma, the most serious type of skin cancer, develops in the cells (melanocytes) that produce melanin — the pigment that gives your skin its color. Melanoma can also form in your eyes and, rarely, in internal organs, such as your intestines.
The exact cause of all melanomas isn’t clear, but exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation from sunlight or tanning lamps and beds increases your risk of developing melanoma.
Donor requirements for participation:
- You must be clinically diagnosed by a medical professional. Confirmation of the diagnosis and/or treatment must be verified with your physician.
- Be pre-screened to determine eligibility.
- You’re willing to donate plasma through the apheresis process.
- You must have a photo ID and be able to provide your social security number or proof of citizenship.
- You must be at least 18 years old.
- You must weight at least 110 lbs.
- You must disclose if you have ever been diagnosed with Hepatitis C and/or HIV.
For questions and concerns about requirements or participation, contact us at (833) GO-4-CURE.
Symptoms
Melanomas can develop anywhere on your body. They most often develop in areas that have had exposure to the sun, such as your back, legs, arms and face. Signs of melanoma include changes in an existing mole (looking for ABCDE: asymmetrical shape, irregular border, changes in color, increased diameter, and evolving mole) and development of new pigment or unusual-looking growth on the skin.
Treatment
Treatment for melanoma that has not spread includes surgical removal of the melanoma. Treatments for melanoma that has spread beyond the skin may include chemotherapy, radiation, and targeted therapy.
This information is not meant for clinical diagnosis, but as an educational resource derived from Mayo Clinic.
Living with a chronic illness can pose great challenges to your daily activity. Being proactive with treatment and donating to research can be a beneficial addition to your routine management. Discovering that you have a disease can be overwhelming with many unanswered questions and concerns. One that may come to mind is “how can I help someone else that may go the same process and struggles that I have experienced?” You can help by becoming a Specialty Antibody donor!
Participating in research allows scientists and clinicians find new treatments, tests and quicker diagnostic methods to improve patient outcomes and, hopefully, prevent the disease in the future.

DO NOT SELL OR SHARE MY INFORMATION
M-Th: 7 AM-3 PM
F: 8:30 AM to 10:30 AM
Programs:
Whole Blood, Plasmapheresis, White Blood Cells
M-F: 8:30 AM to 4 PM
Programs:
Whole Blood, White Blood Cells
M-F: 8:30 AM to 4 PM
Programs:
Whole Blood, White Blood Cells
M-F: 6 AM to 12 PM
Programs:
Whole Blood, White Blood Cells
M-F: 7 AM to 3:30 PM
Programs:
Whole Blood, White Blood Cells, Bone Marrow
M-Th: 8 AM to 5 PM
F: 8 AM - 2 PM
Programs: Whole Blood, White Blood Cells
M-Th: 8:30 AM to 3 PM
F: 8 AM to 12 PM
Programs:
Whole Blood, White Blood Cells
M-Th: 7 AM to 3 PM
F: 7 AM to 12 PM
Programs:
Whole Blood